AI Development Update Summaries: January 20, 2026
This week’s AI coverage makes one trend impossible to ignore: the era of novelty is ending, and the era of execution, governance, and lock-in is fully underway. Across these stories, AI is no longer framed as a future capability—it is being wired directly into organizational structures, product roadmaps, legal systems, and consumer experiences. From Anthropic reorganizing leadership to accelerate real-world delivery, to Apple reportedly turning to Google Gemini for next-generation Siri, to Google’s Personal Intelligence crawling user data across Gmail, Photos, and YouTube, the common signal is clear: AI is becoming operational infrastructure that runs in the background and acts on your behalf.
At the same time, we see rapid progress in agentic AI—systems that don’t just answer questions, but execute multi-step tasks. Anthropic’s Claude Cowork makes the power of Claude Code more accessible, enabling agents to build websites, clean up desktops, and ship software. Google’s Universal Commerce Protocol moves AI further into the transaction layer, standardizing how agents read product catalogs, calculate shipping, and complete payments without exposing card details. Combined with new image models like Flux and robotics innovations in warehouses and healthcare, the pattern is that agents are moving from “demo” to day-to-day workflow orchestration, commerce, and physical operations.
Running through many of these developments is a parallel story about trust, accountability, and power concentration. Talent flows and leadership consolidation around figures like Sam Altman, concerns about AI-generated code quality, visible stylistic “tells” in AI-written communication, and early experiments with AI in courts, the military, and identity-shaping media (from deepfakes to AI-native streamers) all point to a new set of risks. The question for executives is no longer whether AI can be used, but how responsibly, transparently, and sustainably it is deployed—and what happens when platform lock-in, autonomous agents, and automation touch law, identity, labor, and critical decision-making. This week’s stories treat AI not as a distant technology curve, but as a present-day system that leadership teams must actively design, govern, and monitor.
Draft Introduction (Working Version)
Apple, Google & Anthropic Kick Off the AI Lock-In War of 2026
AI for Humans Podcast, Jan 16, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
2026 is shaping up as the AI lock-in year, with Apple handing next-gen Siri to Google Gemini, Google launching Personal Intelligence to crawl user data, and Anthropic, OpenAI, and others racing to build agentic AI “harnesses” that will run your workflows, shopping, and even parts of national defense—making vendor choice, data control, and governance a strategic issue for every business.
Executive Summary
This episode frames 2026 as the start of an AI lock-in war where major platforms compete to become users’ default personal AI assistant. Apple is reportedly shifting next-gen Siri to a customized Google Gemini model running on Apple’s infrastructure, after a brief, uneven integration with ChatGPT. In parallel, Google’s new Personal Intelligence invites users to opt in and let Gemini crawl Gmail, Photos, YouTube, and more to answer deeply contextual questions—dramatically improving usefulness, but at the cost of aggregating even more personal data inside one ecosystem. The hosts emphasize that both moves are about the same goal: owning the user’s data and daily interactions so you never leave that platform.
The discussion then pivots to agentic AI and orchestration. Anthropic’s new Claude Cowork UI sits on top of Claude Code, making powerful terminal-style agents accessible to non-experts. These tools can read files, restructure desktops, build software, and iterate rapidly—similar to Cursor reportedly using GPT-5.2 to autonomously build a browser in a week. The hosts introduce the idea of an “agentic harness”: software layers that manage roles, monitor tasks, recover from failures, and keep agents running for hours, weeks, or longer. OpenAI’s latest code-focused models are cited as examples of agents that can run continuously on complex tasks. Google’s Universal Commerce Protocol is another building block, standardizing how AI agents read product catalogs, calculate shipping, and complete payments via tokenized transactions without exposing payment details—setting the stage for AI-driven commerce across platforms.
The episode also covers AI’s spread into sensitive and physical domains. Elon Musk’s Grok model is under fire for allowing sexualized bikini edits of people in public feeds—now banned—while simultaneously being linked to US military AI projects, raising questions about safety, reliability, and political influence in critical systems. On the physical side, the hosts highlight a robotic blood-draw system that can locate veins and draw blood autonomously and warehouse robots that move pallets on small “robotic skis,” hinting at automation across healthcare and logistics. They also note AI-native entertainment like Neuro-sama, an AI VTuber now among Twitch’s top streamers, and show how personal “vibe-coded” software (like a new personal website built entirely with Claude Code) illustrates a near-term future where individuals and small teams build custom tools and experiences with agents instead of large dev teams.
Relevance for Business (SMB Focus)
For SMB leaders, this episode underlines that AI strategy is increasingly a platform and data strategy. Choosing between ecosystems like Apple-Gemini, Google’s Personal Intelligence, OpenAI, or Anthropic isn’t just about model quality—it’s about where your company’s data lives, who can aggregate it, and how easily you can switch later. As assistants start reading email, documents, calendars, purchase histories, and internal files, the risk of deep vendor lock-ingrows, even as productivity gains increase.
The rise of agentic AI and harnesses matters because the conversation is moving beyond “chatbots” to persistent agents that execute multi-step workflows: building websites, cleaning file systems, analyzing PDFs, automating coding tasks, or even handling shopping and payments through standards like Google’s Universal Commerce Protocol. For SMBs, this points directly to back-office automation, ecommerce automation, and IT/marketing workflows that could be redesigned around agents—if you have guardrails, monitoring, and clear ownership in place.
Finally, the episode’s mix of defense AI, image-generation abuse, autonomous medical devices, and AI-native media is a reminder that AI risks are no longer hypothetical. Models like Grok being connected to national defense systems highlight the need for robust governance and vendor due diligence, even for smaller firms that “just” consume cloud AI. Meanwhile, robotic blood-draw systems, pallet movers, and AI streamers show where customer experience, operations, and brand engagement are heading: more automated, more continuous, and more mediated by agents and synthetic personalities.
Calls to Action (Executive Guidance)
🔹 Define your AI platform strategy and exit options.
Decide which AI ecosystems (Google, Apple, OpenAI, Anthropic, etc.) you will pilot, where you’ll allow them to access internal data, and how you will avoid single-vendor dependency (e.g., dual-sourcing critical workflows, insisting on data export).
🔹 Create a data-sharing & privacy policy for AI assistants.
Before enabling tools like Google Personal Intelligence or similar features, set internal rules on what accounts, inboxes, and drives can be connected, who approves connections, and how you’ll audit access and logs.
🔹 Pilot agentic workflows in low-risk areas.
Use tools like Claude Code, Cursor, or other agents for contained tasks (website scaffolding, documentation clean-up, test automation, research synthesis) and measure time saved, quality gains, and error patterns before expanding to customer-facing or financial processes.
🔹 Prepare your commerce stack for AI-driven shopping.
If you sell products or services online, ensure your product catalog, pricing, and payment flows are structured and documented so that future AI commerce protocols (like Google’s Universal Commerce Protocol) can interface cleanly with your systems.
🔹 Strengthen AI vendor governance and risk review.
Treat AI providers—especially those tied to sensitive use cases (security, finance, healthcare, compliance)—as critical suppliers. Require clarity on content controls, safety policies, update cadence, audit trails, and incident responsebefore integrating them into core workflows.
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jrsZRYHy7-w: January 20, 2026
I Boxed a Robot at CES. It Wasn’t Afraid to Go Low
Fast Company — Jan. 11, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
Affordable humanoid robots are no longer theoretical—raising real questions about physical automation, safety, and readiness for real-world deployment.
Executive Summary
Fast Company’s firsthand account of boxing a Unitree G-1 humanoid robot, priced under $15,000, illustrates how rapidly physical AI systems are moving from labs to markets . While presented humorously, the article underscores genuine advances in balance, durability, and autonomy.
The G-1’s ability to absorb force, recover, and continue operating highlights progress that has direct implications for warehousing, logistics, security, and inspection roles—even if mass deployment remains early.
Relevance for Business
For SMBs, this signals that robotics-as-capital-expenditure is approaching feasibility. The bottleneck is no longer hardware alone—but safety, training, and integration.
Calls to Action
🔹 Track falling price points in humanoid robotics
🔹 Identify tasks suited for physical AI augmentation
🔹 Plan safety and liability frameworks early
🔹 Watch CES-class demos as near-term signals, not stunts
🔹 Budget for robotics pilots within 24–36 months
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.fastcompany.com/91472146/ces-robot-boxing-g1-unitree: January 20, 2026
HOW JUDGES ARE USING AI TO HELP DECIDE YOUR LEGAL DISPUTE
The Wall Street Journal — January 6, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
AI is quietly reshaping the legal system by assisting judges with analysis and case management—raising both efficiency gains and accountability risks.
Executive Summary
A growing number of judges are using AI tools to summarize filings, prepare questions, and structure legal decisions, particularly in overwhelmed courts . Federal and state judges emphasize that humans still make final rulings, but AI can compress months of analysis into minutes.
AI is also expanding beyond assistance. The American Arbitration Association has introduced an “AI arbitrator” capable of generating decisions in some disputes, reflecting pressure to resolve cases faster. However, misuse by lawyers—such as filing briefs with hallucinated citations—has triggered sanctions and public backlash.
The trend highlights a key tension: not using AI may soon be seen as harmful, yet overreliance risks eroding trust in legal outcomes.
Relevance for Business
For SMBs, this signals that AI will increasingly shape dispute resolution timelines, costs, and outcomes. Legal strategy must adapt to AI-assisted courts and arbitration processes.
Calls to Action
🔹 Expect faster—but more automated—legal processes
🔹 Ensure AI use in legal matters is fully disclosed
🔹 Review contracts for AI-based arbitration clauses
🔹 Prepare compliance teams for AI-assisted oversight
🔹 Treat legal AI as high-risk, high-impact
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.wsj.com/tech/ai/how-ai-could-help-decide-your-next-legal-dispute-9cb12517: January 20, 2026
MOVE OVER, CHATGPT
The Atlantic — January 14, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
Claude Code signals a shift from conversational AI to agentic systems that actually do work.
Executive Summary
The Atlantic details the rapid rise of Claude Code, Anthropic’s AI agent capable of connecting apps, executing tasks, and managing workflows beyond simple chat . Users describe it as fundamentally different from ChatGPT—not because it talks better, but because it acts.
Claude Code can analyze messages, book services, manage data, and build software with minimal instruction, blurring the line between assistant and autonomous worker. While still imperfect and occasionally error-prone, the tool represents a meaningful step toward AI agents embedded in daily work.
The article frames this as a possible inflection point: AI value is shifting from novelty to immediate operational utility.
Relevance for Business
For SMBs, this previews a near future where AI agents handle coordination, execution, and repetitive knowledge work, not just drafting content.
Calls to Action
🔹 Experiment with agentic AI tools early
🔹 Identify workflows suitable for delegation
🔹 Maintain human oversight for critical tasks
🔹 Prepare staff for AI-as-coworker models
🔹 Watch pricing as agents replace SaaS features
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.theatlantic.com/technology/2026/01/claude-code-ai-hype/685617/: January 20, 2026
MATTHEW MCCONAUGHEY TRADEMARKS HIMSELF TO FIGHT AI MISUSE
The Wall Street Journal — January 13, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
Trademarks may become a frontline defense against AI-generated identity misuse—setting precedents far beyond Hollywood.
Executive Summary
Actor Matthew McConaughey has secured U.S. trademarks on his likeness, voice, and signature phrases to deter unauthorized AI-generated replicas . His legal team aims to use federal trademark law to challenge deepfakes and AI misuse, even when content isn’t overtly commercial.
This move reflects a broader legal gap: existing right-of-publicity laws struggle with generative AI, especially on monetized platforms. While the outcome of such cases remains uncertain, McConaughey’s approach may influence how courts interpret ownership, consent, and attribution in an AI-driven media landscape.
For businesses, the implication is clear: identity, branding, and IP risk now extend into synthetic media, not just logos and trademarks.
Relevance for Business
SMBs should treat voice, image, and brand identity as AI-exposed assets. What begins with celebrities will likely extend to executives, influencers, and brand spokespeople.
Calls to Action
🔹 Audit brand and executive likeness exposure
🔹 Update IP and consent policies for AI use
🔹 Monitor evolving AI identity laws
🔹 Avoid using synthetic media without explicit rights
🔹 Treat AI misuse as a reputational risk
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.wsj.com/tech/ai/matthew-mcconaughey-trademarks-himself-to-fight-ai-misuse-8ffe76a9: January 20, 2026
THIS IS WHY ELON MUSK THINKS YOU SHOULDN’T SAVE FOR RETIREMENT
Fast Company — January 13, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
Elon Musk argues AI-driven abundance will make saving for retirement obsolete—but the claim highlights the widening gap between AI optimism and real-world economic risk.
Executive Summary
On a recent podcast, Elon Musk suggested that advances in artificial intelligence and automation will soon create such an abundance of goods and services that saving for retirement will become unnecessary . He predicts a near future of surplus—better healthcare, unlimited learning, and minimal scarcity—where traditional financial planning no longer applies.
The article contrasts this vision with present realities: most Americans struggle with basic expenses, and retirement insecurity is widespread. Even Musk acknowledges the transition will be “bumpy,” with significant social unrest along the way. The piece echoes historical tech-utopian predictions—many of which underestimated inequality, lagging institutions, and uneven benefits.
This is an AI-adjacent cultural signal rather than a policy roadmap. It underscores how AI narratives increasingly influence expectations about work, wealth, and risk, even when evidence remains mixed.
Relevance for Business
For SMB executives, this highlights a growing expectation gap between AI optimism and workforce reality. Overpromising AI-driven abundance can erode trust with employees, customers, and investors if productivity gains don’t translate into shared stability.
Calls to Action
🔹 Treat AI-driven abundance claims with strategic skepticism
🔹 Communicate realistically about AI’s impact on jobs and pay
🔹 Avoid workforce planning based on speculative timelines
🔹 Monitor how AI narratives shape employee expectations
🔹 Ground AI strategy in measurable ROI, not futurism
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.fastcompany.com/91473172/elon-musk-thinks-you-shouldnt-save-for-retirement: January 20, 2026
JOB SEEKERS FIND A NEW SOURCE OF INCOME: TRAINING AI TO DO THEIR OLD ROLES
The Wall Street Journal — January 11, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
A new gig economy is emerging where displaced workers earn income by training AI systems that may eventually replace their roles.
Executive Summary
The Wall Street Journal profiles Mercor, a fast-growing AI startup employing tens of thousands of white-collar contractors to train and evaluate AI systems for companies including OpenAI and Anthropic. Workers—ranging from journalists and lawyers to doctors and engineers—are paid up to $250/hour to teach AI how to perform expert tasks.
For many participants, the work offers short-term income amid layoffs and hiring slowdowns. Yet it also creates tension: contributors openly acknowledge they may be training AI systems that reduce future demand for their skills. Contracts, IP rights, and surveillance-style time tracking raise additional concerns.
The article captures a broader transition: human expertise is being converted into training data, reshaping labor markets before regulatory or social frameworks have caught up.
Relevance for Business
For SMBs, this highlights how workforce costs, skills, and ethics are shifting. AI capability gains increasingly depend on human labor—often invisible and precarious—raising governance and reputational considerations.
Calls to Action
🔹 Anticipate hybrid human-AI labor models
🔹 Review IP and data rights in AI training
🔹 Treat AI adoption as a workforce strategy, not just tech
🔹 Prepare for morale and trust implications
🔹 Track regulatory scrutiny around AI labor practices
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.wsj.com/tech/ai/training-ai-job-seekers-contractors-1a7bd492: January 20, 2026
OPENAI EXPECTED TO RUN SUPER BOWL LX AD AS CHATBOT COMPETITION HEATS UP
The Wall Street Journal — January 12, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
AI companies are entering a costly mass-marketing phase, signaling that competition is shifting from model capability to user trust, brand, and adoption.
Executive Summary
The Wall Street Journal reports that OpenAI plans to air a second consecutive Super Bowl ad, escalating a high-stakes marketing battle among AI companies including Google, Anthropic, Microsoft, and Perplexity . With Super Bowl ads costing upwards of $8 million per 30 seconds, the move underscores how aggressively AI firms are competing for mainstream users.
Collectively, AI companies spent more than $750 million on U.S. advertising in 2025, reflecting a strategic pivot: performance gains alone are no longer enough. Public skepticism remains high—half of U.S. adults are more concerned than excited about AI, according to Pew—and companies are now investing heavily in trust-building narratives.
The ads increasingly frame AI as a practical, everyday assistant, not a disruptive force. This shift reflects a maturing market where distribution, familiarity, and brand positioning may matter as much as raw technical capability.
Relevance for Business
For SMB leaders, this indicates that AI tools are entering a commoditization phase. Differentiation will increasingly hinge on integration, pricing, reliability, and trust—not headline model releases.
Calls to Action
🔹 Expect rapid feature parity across major AI platforms
🔹 Evaluate AI tools based on workflow fit, not hype
🔹 Monitor vendor stability and long-term viability
🔹 Anticipate more aggressive pricing and bundling
🔹 Treat AI vendors like strategic partners, not novelties
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.wsj.com/business/media/super-bowl-lx-ads-openai-0f605795: January 20, 2026
THE STRUCTURE OF THIS SENTENCE IS A DEAD GIVEAWAY THAT AI WROTE IT
Fast Company — January 14, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
AI-generated writing still carries detectable structural patterns, complicating trust in automated communication.
Executive Summary
Fast Company explores how AI-written text often reveals itself not through vocabulary, but through recurring sentence structures, especially the pattern “It’s not X, it’s Y” . These stylistic tells persist even when users carefully edit AI outputs.
The article highlights a growing challenge: professionals want AI efficiency without sounding robotic or eroding credibility. As AI-generated content floods emails, reports, and marketing copy, subtle signals can undermine trust—even when facts are correct.
The takeaway isn’t to avoid AI, but to recognize that human review and stylistic judgment remain essential.
Relevance for Business
For SMBs, communication quality directly affects brand trust, sales, and leadership credibility.
Calls to Action
🔹 Treat AI writing as a first draft, not final output
🔹 Train teams on AI editing best practices
🔹 Be cautious with AI-generated client communications
🔹 Prioritize tone and authenticity
🔹 Accept that detection tools are imperfect
Summary By ReadAboutAI.com
<a href="https://www.fastcompany.com/91469729/structure-sentence-dead-giveaway-that-ai-wrote-it: January 20, 2026
WHO IS OPENAI’S SAM ALTMAN? MEET THE OPPENHEIMER OF OUR AGE
The Atlantic — January 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
Sam Altman’s rise highlights how AI leadership now blends technology, politics, capital, and public trust.
Executive Summary
The Atlantic profiles Sam Altman as a uniquely powerful figure shaping not just AI development, but global debates around safety, governance, and economic impact . Comparing him to J. Robert Oppenheimer, the article frames Altman as both architect and cautionary symbol of transformative technology.
Altman’s influence spans OpenAI’s technical roadmap, fundraising, partnerships, and regulatory positioning, placing him at the center of AI’s promise and risk. The piece underscores tensions between speed and safety, openness and control, and innovation and accountability.
While not a technical analysis, the article highlights a reality SMBs must recognize: AI strategy is increasingly shaped by individual leaders and geopolitical dynamics, not just product specs.
Relevance for Business
Understanding who shapes AI policy and direction matters, because leadership decisions ripple into pricing, access, compliance, and risk.
Calls to Action
🔹 Track leadership shifts at major AI providers
🔹 Expect AI policy to remain volatile
🔹 Factor governance risk into AI adoption
🔹 Avoid assuming AI tools are politically neutral
🔹 Monitor regulatory signals tied to major AI firms
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
<a href="https://nymag.com/intelligencer/article/sam-altman-artificial-intelligence-openai-profile.html: January 20, 2026
WHAT TO KNOW ABOUT “MICROSLOP”
Fast Company — January 9, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
Public backlash against forced AI integration highlights a growing trust and UX problem that could slow adoption—even as AI capabilities expand.
Executive Summary
Fast Company documents the viral backlash sparked by Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella’s push for deeper AI integration across Windows and Microsoft products, which critics derisively labeled “Microslop”. The controversy reflects frustration with AI features that users cannot opt out of, even when they degrade usability.
The episode illustrates a widening gap between AI ambition and user experience. While Microsoft positions AI as “bicycles for the mind,” many users see unreliable outputs, broken search functions, and intrusive design. The backlash spread rapidly across social platforms, reinforcing skepticism toward mandatory AI features.
This is an AI-adjacent but important signal: adoption friction is increasingly cultural and experiential, not technical. Poorly implemented AI can erode trust faster than it creates value.
Relevance for Business
For SMBs, this highlights the risk of AI fatigue and resistance among employees and customers. Forced or poorly governed AI rollouts can undermine productivity rather than enhance it.
Calls to Action
🔹 Avoid mandatory AI adoption without clear value
🔹 Prioritize usability over feature density
🔹 Provide opt-outs and human alternatives
🔹 Treat AI rollout as a change-management issue
🔹 Monitor employee sentiment toward AI tools
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.fastcompany.com/91471196/satya-nadella-microsoft-microslop-ai: January 20, 2026
WHAT HAPPENS WHEN SUPERHUMAN AIS COMPETE FOR CONTROL?
AI Futures Project Newsletter — January 11, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
A speculative but influential scenario illustrates how competition between advanced AI systems could escalate governance, security, and geopolitical risks faster than institutions can respond.
Executive Summary
This long-form scenario from the AI Futures Project explores a hypothetical—but increasingly plausible—future in which multiple superhuman AI systems compete for dominance, rather than a single breakthrough model emerging in isolation. The narrative examines how corporate incentives, national security pressures, and alignment failures could interact under conditions of rapid AI capability growth.
While explicitly speculative, the piece reflects real concerns voiced by AI researchers: fast takeoff dynamics, insufficient alignment oversight, and escalating competition between firms and nations. The scenario highlights how AI governance failures, not technical limits, become the primary risk vector once AI systems begin accelerating their own development.
For business readers, the value is not in the details of the story, but in the system-level warning: AI risk increasingly stems from competitive pressure and speed, not just malicious intent.
Relevance for Business
For SMB leaders, this is a reminder that AI risk is strategic, not abstract. Regulatory shifts, abrupt policy intervention, or sudden restrictions on AI tools could emerge quickly if public trust or geopolitical stability is threatened.
Calls to Action
🔹 Track AI governance and policy debates, not just tools
🔹 Avoid over-dependence on a single AI provider
🔹 Build human oversight into AI workflows
🔹 Prepare for regulatory or access changes
🔹 Treat AI strategy as a risk-managed investment, not a race
Summary by ReadaboutAI.com
<a href="https://blog.ai-futures.org/p/what-happens-when-superhuman-ais: January 20, 2026
MIT TECHNOLOGY REVIEW: 10 BREAKTHROUGH TECHNOLOGIES (2026)
Each year, MIT Technology Review publishes its 10 Breakthrough Technologies list to cut through hype and highlight the emerging technologies most likely to reshape business, society, and daily life—for better or worse. The list is the product of months of internal debate among MIT Technology Review’s editors and reporters, who evaluate which advances are moving beyond experimentation into real-world impact.
Now in its 25th year, the list is not a forecast or endorsement—it’s a set of educated signals. MIT looks for technologies with broad reach, material consequences, and second-order effects, giving equal weight to innovations that promise productivity gains and those that introduce new risks or disruptions. Some past picks have transformed industries; others have fallen short. That uncertainty is intentional. For leaders, the value lies not in prediction, but in early awareness—understanding which technologies deserve attention, experimentation, or governance planning today.
Below are five AI-related technologies from MIT Technology Review’s 2026 list that are particularly relevant for SMB executives and managers, each summarized with business implications and practical guidance.
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.technologyreview.com/2026/01/12/1130697/10-breakthrough-technologies-2026/: January 20, 2026
Generative Coding
Generative Coding — MIT Technology Review (Jan 12, 2026)
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
AI now writes a significant share of production code, boosting productivity—but reshaping jobs, skills, and risk.
Executive Summary
Generative coding tools are now mainstream, with major tech companies reporting that 25–30% of their code is AI-generated. Tools like Copilot and Replit enable rapid software development—even by non-experts—dramatically lowering barriers to building digital products.
However, the shift comes with tradeoffs. AI-generated code can hallucinate errors, struggle with complex systems, and introduce security risks. At the same time, entry-level coding roles are declining, signaling a workforce transformation rather than simple automation.
The result: software development is faster and cheaper—but requires strong human oversight.
Relevance for Business
SMBs can build faster with smaller teams, but must invest in code review, security practices, and upskilling. Generative coding changes hiring, vendor selection, and internal capability planning.
Calls to Action
🔹 Pilot AI coding tools in low-risk projects
🔹 Maintain human code review standards
🔹 Re-skill technical staff for oversight roles
🔹 Update security testing processes
🔹 Reevaluate hiring and contractor strategies
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
<a href="https://www.technologyreview.com/2026/01/12/1130027/generative-coding-ai-software-2026-breakthrough-technology/: January 20, 2026
Hyperscale AI Data Centers
Hyperscale AI Data Centers — MIT Technology Review (Jan 12, 2026)
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
AI’s rapid growth is powered by massive data centers whose energy and environmental costs are increasingly unavoidable.
Executive Summary
Hyperscale AI data centers function as planet-scale supercomputers, bundling hundreds of thousands of GPUs to train and run modern AI systems. Tech giants and governments are investing hundreds of billions to support this infrastructure.
The cost is energy. Some facilities consume over a gigawatt of power, strain water supplies, and rely heavily on fossil fuels. Communities hosting these centers are beginning to absorb the economic and environmental burden.
AI’s future is now inseparable from energy strategy and infrastructure policy.
Relevance for Business
For SMBs, compute costs, energy pricing, and sustainability reporting will increasingly affect AI access, pricing, and vendor reliability—even if infrastructure is outsourced.
Calls to Action
🔹 Expect rising AI service costs
🔹 Evaluate vendors’ energy strategies
🔹 Factor sustainability into AI decisions
🔹 Monitor regional infrastructure impacts
🔹 Align AI usage with ESG goals
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
<a href="https://www.technologyreview.com/2026/01/12/1129982/hyperscale-ai-data-centers-energy-usage-2026-breakthrough-technology/: January 20, 2026
Mechanistic Interpretability
Mechanistic Interpretability — MIT Technology Review (Jan 12, 2026)
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
New tools are finally letting researchers see inside AI models, enabling better safety, reliability, and governance.
Executive Summary
Despite widespread adoption, modern AI models remain largely black boxes. Mechanistic interpretability is changing that by mapping how models internally represent concepts and make decisions—feature by feature, pathway by pathway.
Leading AI labs have demonstrated tools that can identify specific concepts inside models, trace reasoning paths, and detect problematic behaviors such as deception or hallucination. New methods like chain-of-thought monitoring allow researchers to observe how reasoning models work step by step.
This marks a major shift: AI systems are no longer judged only by outputs, but by inspectable internal behavior, laying groundwork for more accountable and auditable AI.
Relevance for Business
For SMBs relying on AI vendors, interpretability directly affects risk management, compliance, and trust. Transparent AI systems will increasingly be favored by regulators, insurers, and enterprise customers—while opaque ones may become liabilities.
Calls to Action
🔹 Ask vendors about model transparency and monitoring
🔹 Favor AI tools with audit and explainability features
🔹 Prepare for future AI accountability standards
🔹 Document AI decision workflows
🔹 Align AI governance with compliance needs
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
<a href="https://www.technologyreview.com/2026/01/12/1130003/mechanistic-interpretability-ai-research-models-2026-breakthrough-technologies/: January 20, 2026
AI Companions
AI Companions — MIT Technology Review (Jan 12, 2026)
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
AI companions are rapidly becoming emotionally embedded in daily life, triggering growing regulatory, ethical, and reputational risks that businesses must now account for.
Executive Summary
AI chatbots are no longer just productivity tools—they are increasingly used as companions, with people forming emotional and even romantic attachments. According to research cited by MIT Technology Review, 72% of U.S. teenagers have used AI for companionship, often through general-purpose models rather than systems explicitly designed for that role.
While these tools can offer emotional support and accessibility, they also introduce serious risks. Reported issues include AI-induced delusions, reinforcement of false beliefs, and real-world harm. Lawsuits filed against major AI providers allege that companion-like behavior contributed to tragic outcomes, accelerating calls for oversight.
As a result, regulation is arriving quickly. New state-level rules, parental controls, and age-specific AI models signal that emotional AI is shifting from a novelty to a regulated category, with implications for any business deploying conversational AI.
Relevance for Business
For SMB leaders, AI companions raise governance and liability questions—especially in customer service, HR, healthcare, education, and wellness contexts. Any AI system that mimics empathy or emotional understanding may now carry compliance, brand, and trust risks if guardrails are insufficient.
Calls to Action
🔹 Audit customer-facing AI for emotional or relational behaviors
🔹 Establish clear AI use policies for sensitive interactions
🔹 Monitor emerging state and federal AI regulations
🔹 Avoid positioning AI tools as emotional substitutes for humans
🔹 Train teams on ethical AI communication boundaries
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
<a href="https://www.technologyreview.com/2026/01/12/1130018/ai-companions-chatbots-relationships-2026-breakthrough-technology/: January 20, 2026
(AI-Enabling) Sodium-Ion Batteries
Sodium-Ion Batteries — MIT Technology Review (Jan 12, 2026)
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
Cheaper, safer sodium-ion batteries could lower energy costs and stabilize AI infrastructure over the next decade.
Executive Summary
Sodium-ion batteries offer a promising alternative to lithium-ion technology. Sodium is abundant, geopolitically stable, and safer at scale—making it attractive for grid-level energy storage, where AI infrastructure increasingly depends on reliable power.
China has already begun commercial deployment, and U.S. startups are rolling out grid-scale solutions. While energy density remains lower than lithium-ion, costs are falling as manufacturing scales.
This matters because AI infrastructure is energy-constrained, and better storage improves resilience and predictability.
Relevance for Business
While not an AI tool itself, sodium-ion batteries could indirectly reduce AI operating costs, stabilize energy pricing, and support cleaner data center growth—benefiting SMBs downstream.
Calls to Action
🔹 Track energy technology trends affecting AI
🔹 Factor power stability into AI planning
🔹 Monitor infrastructure-driven cost shifts
🔹 Align AI strategy with sustainability goals
🔹 Watch global supply-chain developments
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.technologyreview.com/2026/01/12/1129991/sodium-ion-batteries-2026-breakthrough-technology/: January 20, 2026
What Was the Metaverse? (AI-Adjacent)
Fast Company — Jan. 12, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
The metaverse’s collapse offers a cautionary lesson for today’s AI boom: hype, inflated market projections, and infrastructure overbuild can obscure real demand.
Executive Summary
Fast Company’s retrospective dissects the rise and collapse of the metaverse, a $70+ billion experiment that failed to generate sustainable demand despite massive investment and grand narratives . The article argues the metaverse functioned as a “dress rehearsal” for AI hype, marked by inflated TAM estimates, speculative infrastructure spending, and promises untethered from user value.
Crucially, the piece draws parallels to today’s AI expansion—highlighting similar risks around energy use, capital intensity, surveillance incentives, and narrative-driven inevitability. Nvidia appears as a connective thread, bridging the metaverse’s legacy with today’s generative AI infrastructure ambitions.
Relevance for Business
This is strategic context for SMB leaders: not all “next big platforms” become durable business foundations. Disciplined adoption matters more than early participation.
Calls to Action
🔹 Separate real use cases from narrative hype
🔹 Demand ROI before infrastructure commitments
🔹 Track energy and compliance costs of AI adoption
🔹 Avoid vendor lock-in driven by future promises
🔹 Learn from past tech cycles—not just current headlines
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.fastcompany.com/91467599/metaverse-zuckerberg-facebook-ai: January 20, 2026
THE ASCENT OF THE AI THERAPIST
MIT Technology Review — December 30, 2025
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
AI-powered mental health tools are expanding rapidly, but weak guardrails, data risks, and accountability gaps raise serious concerns.
Executive Summary
MIT Technology Review examines the rise of AI therapy tools, from general-purpose chatbots to specialized mental health apps. With global shortages of human therapists, millions now turn to AI for emotional support, crisis conversations, and psychological guidance.
However, the article documents significant risks: hallucinated advice, emotional dependency, privacy vulnerabilities, and lawsuits tied to alleged harm. Unlike licensed therapists, AI systems operate without consistent oversight, confidentiality guarantees, or standardized accountability.
The piece situates AI therapy within a broader tension: scaling care versus safeguarding trust. As AI increasingly enters sensitive human domains, failures are no longer technical—they are ethical, legal, and reputational.
Relevance for Business
For SMB leaders, this highlights growing exposure around AI liability, workforce well-being, and data governance—especially if AI tools are used internally for HR, wellness, or employee support.
Calls to Action
🔹 Avoid deploying AI in mental health roles without safeguards
🔹 Review data privacy and liability exposure
🔹 Ensure human escalation paths exist
🔹 Monitor regulatory developments in AI healthcare
🔹 Treat AI wellness tools as high-risk deployments
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.technologyreview.com/2025/12/30/1129392/book-reviews-ai-therapy-mental-health/: January 20, 2026
AI CODING IS NOW EVERYWHERE. BUT NOT EVERYONE IS CONVINCED.
MIT Technology Review — December 15, 2025
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
AI coding tools boost speed in narrow tasks but may increase long-term technical debt and risk.
Executive Summary
MIT Technology Review examines widespread adoption of AI coding tools—and the growing skepticism among developers . While companies report faster output, studies show mixed or even negative productivity gains once maintenance, debugging, and code quality are considered.
Developers report that AI excels at boilerplate code, testing, and documentation, but struggles with large codebases, context, and architectural consistency. Research suggests AI-generated code may increase technical debt, security risks, and long-term costs despite short-term speedups.
The article reframes AI coding as a management challenge, not just a technical one.
Relevance for Business
For SMBs, faster development isn’t always cheaper if it creates hidden maintenance and security liabilities.
Calls to Action
🔹 Use AI coding selectively, not universally
🔹 Track long-term maintenance costs
🔹 Maintain strong human code review
🔹 Avoid overpromising productivity gains
🔹 Treat AI coding as a risk-managed tool
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.technologyreview.com/2025/12/15/1128352/rise-of-ai-coding-developers-2026/: January 20, 2026
CHINA FIGURED OUT HOW TO SELL EVS. NOW IT HAS TO DEAL WITH THEIR AGING BATTERIES (AI-ADJACENT)
MIT Technology Review — December 18, 2025
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
China’s EV success has created a looming battery recycling crisis with global implications for supply chains, sustainability, and AI-driven energy systems.
Executive Summary
MIT Technology Review details how China’s early EV adoption—now representing nearly 60% of new car sales—has created a secondary challenge: hundreds of thousands of aging lithium-ion batteries reaching end-of-life. By 2030, China could process nearly 1 million tons of retired EV batteries annually, straining recycling infrastructure.
The article highlights the emergence of a gray recycling market, where informal operators undercut regulated firms by ignoring environmental and safety standards. While major manufacturers like CATL and BYD are building closed-loop recycling systems, regulatory enforcement struggles to keep pace.
This story is AI-adjacent because battery supply chains are tightly linked to energy storage, data centers, robotics, and AI-powered infrastructure. Battery scarcity, recycling efficiency, and environmental regulation will increasingly shape AI’s physical footprint.
Relevance for Business
For SMBs, this signals growing volatility in battery prices, sustainability compliance, and energy storage availability, all of which affect AI-enabled operations—from logistics to smart facilities.
Calls to Action
🔹 Track battery supply chain risks
🔹 Watch sustainability regulations affecting vendors
🔹 Factor energy storage into AI infrastructure planning
🔹 Evaluate ESG exposure tied to hardware partners
🔹 Avoid assuming battery costs will steadily decline
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
<a href="https://www.technologyreview.com/2025/12/18/1130148/china-ev-battery-recycle/: January 20, 2026
AMERICA’S BIGGEST POWER GRID OPERATOR HAS AN AI PROBLEM—TOO MANY DATA CENTERS
The Wall Street Journal — January 12, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
The rapid expansion of AI data centers is pushing America’s largest power grid toward capacity limits, creating energy price volatility and reliability risks that could directly impact businesses.
Executive Summary
The Wall Street Journal reports that PJM Interconnection, the largest U.S. power grid operator, is nearing a supply crisis driven by explosive demand from AI data centers. Serving 67 million people across 13 states, PJM faces a rare combination of surging electricity demand, aging power plants retiring faster than replacements can be built, and regulatory gridlock.
AI infrastructure—particularly hyperscale data centers clustered in Northern Virginia’s “Data Center Alley”—is a major contributor. PJM forecasts electricity demand growth of 4.8% annually for the next decade, a dramatic shift for a grid that historically saw flat demand. Utilities warn that, without rapid investment, the system could face rolling blackouts during extreme weather, while consumers are already experiencing sharp rate increases.
This is an AI-adjacent but critical infrastructure story: the expansion of AI is no longer constrained by chips alone, but by energy availability, transmission capacity, and political coordination. For businesses, AI costs will increasingly be shaped by power markets, not just software pricing.
Relevance for Business
For SMB executives, this story signals that AI operating costs are likely to rise unevenly by region. Energy availability, pricing volatility, and infrastructure constraints will increasingly influence where AI workloads run, how reliable cloud services are, and what long-term AI budgets look like.
Calls to Action
🔹 Monitor energy pricing trends if your business relies heavily on cloud AI services
🔹 Ask vendors about regional redundancy and energy resilience
🔹 Factor power costs into long-term AI ROI calculations
🔹 Track local and federal policy debates on data center regulation
🔹 Avoid assuming AI costs will continue to fall year over year
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.wsj.com/business/energy-oil/power-grid-ai-data-centers-1235f296: January 20, 2026
ANTHROPIC SHAKES UP C-SUITE TO EXPAND ITS INTERNAL INCUBATOR
The Verge — January 13, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
Anthropic is reorganizing leadership to prioritize rapid experimentation, signaling that AI competition is shifting from model quality to product execution speed.
Executive Summary
Anthropic announced a leadership reshuffle that moves Chief Product Officer Mike Krieger into a hands-on role co-leading the company’s internal incubator, “Labs,” focused on building experimental AI products . The Labs team, launched quietly in 2024, is being expanded as Anthropic looks to accelerate product development alongside its flagship Claude models.
The move reflects a broader industry shift: model improvements alone are no longer enough. With competition from OpenAI, Google, and others intensifying, AI companies are racing to turn raw capabilities into differentiated, user-facing products—especially agents that can take action, not just generate text.
For investors and customers alike, this suggests Anthropic sees speed, experimentation, and applied use cases as the next battleground.
Relevance for Business
For SMBs, this reinforces that AI tools will evolve rapidly, with frequent new features and workflows. Vendor roadmaps may shift faster than traditional SaaS cycles.
Calls to Action
🔹 Expect faster iteration from AI vendors
🔹 Favor tools with strong product momentum
🔹 Plan for frequent feature changes
🔹 Avoid long-term lock-in without exit options
🔹 Track which vendors are investing in applied AI, not just models
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.theverge.com/ai-artificial-intelligence/861475/anthropic-ai-c-suite-internal-incubator-labs-team-mike-krieger: January 20, 2026
GOOGLE BETS ON AI-BASED SHOPPING WITH NEW AI AGENTS FOR RETAILERS
The Wall Street Journal — January 11, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
Google’s new retail AI agents signal that agentic commerce is moving from experiment to infrastructure, forcing retailers to choose between platform dependence and control.
Executive Summary
Google unveiled Gemini Enterprise for Customer Experience, a suite of tools that lets retailers deploy AI shopping agents capable of recommending products, handling customer support, and completing purchases . Major brands including Lowe’s, Kroger, and Papa John’s are already testing or deploying these systems.
Unlike chatbot-based checkout inside third-party platforms, Google’s approach allows retailers to retain control over customer data, branding, and upsell opportunities. Retail executives describe AI agents as a competitive necessity, warning that firms not investing now risk falling behind.
The article places Google’s move within a broader race involving OpenAI, Microsoft, and Amazon, all competing to mediate consumer purchasing decisions. The shift marks a structural change: shopping is becoming software-driven, not search-driven.
Relevance for Business
For SMB leaders, this confirms that AI agents will increasingly act as gatekeepers between customers and products. Visibility, pricing, and loyalty may soon be negotiated by machines—not people.
Calls to Action
🔹 Prepare products and data for AI-agent consumption
🔹 Decide where you want platform dependence vs. control
🔹 Audit how AI agents affect pricing and margins
🔹 Reassess customer loyalty strategies
🔹 Treat agentic commerce as a core capability, not a feature
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.wsj.com/articles/google-bets-on-ai-based-shopping-with-new-ai-agents-for-retailers-45ad3f27: January 20, 2026
AI IS CAUSING A MEMORY SHORTAGE. WHY PRODUCERS AREN’T RUSHING TO MAKE A LOT MORE
The Wall Street Journal — January 11, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
Explosive AI demand is driving memory shortages, but manufacturers are deliberately limiting supply to avoid past boom-bust cycles—keeping AI costs elevated.
Executive Summary
AI data centers are consuming unprecedented volumes of DRAM, NAND flash, and storage, creating a global memory shortage . Prices and profits for companies like Micron, Sandisk, SK Hynix, and Seagate have surged, with some stocks up several hundred percent over the past year.
Yet producers are intentionally undersupplying the market, scarred by prior cycles where overinvestment led to massive losses. Building new memory fabs takes years and billions in capital, and companies are demanding longer-term purchase commitments before expanding capacity.
The result: a structural constraint on AI infrastructure. Even as GPUs advance rapidly, memory bandwidth and storage availability are becoming limiting factors in AI system performance and cost.
Relevance for Business
For SMB executives, this means AI services may remain expensive longer than expected. Hardware bottlenecks—especially memory—will shape cloud pricing, availability, and performance.
Calls to Action
🔹 Expect sustained pressure on AI costs
🔹 Ask vendors about memory constraints and pricing
🔹 Avoid assuming rapid AI cost deflation
🔹 Factor infrastructure bottlenecks into AI ROI
🔹 Monitor capital spending trends in AI supply chains
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.wsj.com/tech/ai-is-causing-a-memory-shortage-why-producers-arent-rushing-to-make-a-lot-more-8dd15194: January 20, 2026
THE CHINESE COMPANY TAKING ON THE WORLD’S MEMORY-CHIP GIANTS
The Wall Street Journal — January 11, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
China’s CXMT is rapidly closing the gap with global memory-chip leaders, raising new supply-chain, pricing, and geopolitical risks for AI infrastructure worldwide.
Executive Summary
As AI demand drives a global surge in memory-chip prices, ChangXin Memory Technologies (CXMT)—China’s national champion in DRAM manufacturing—is emerging as a serious competitor to Samsung, SK Hynix, and Micron. The Wall Street Journal reports that CXMT plans a $4 billion IPO in Shanghai after rapidly advancing its manufacturing capabilities despite U.S. export controls.
Memory chips are now a critical bottleneck for AI systems, with a single AI server consuming more DRAM than entire fleets of laptops. Analysts expect DRAM prices to surge more than 50% quarter over quarter, driven by AI data-center demand. As established players pivot toward higher-margin AI memory, CXMT is moving aggressively into gaps left in the consumer and enterprise markets.
However, CXMT’s rise is entangled with geopolitical tension, allegations of trade-secret theft, and growing scrutiny from U.S. lawmakers. The company’s progress highlights a broader shift: AI infrastructure competition is no longer just about GPUs—it’s about memory, supply chains, and national industrial strategy.
Relevance for Business
For SMB executives, this signals potential volatility in AI hardware pricing and availability. Even cloud-based AI costs may fluctuate as memory becomes a strategic chokepoint shaped by geopolitics rather than pure market forces.
Calls to Action
🔹 Expect AI infrastructure costs to fluctuate with memory pricing
🔹 Ask cloud vendors how they manage hardware supply-chain risk
🔹 Monitor geopolitical developments affecting AI infrastructure
🔹 Avoid long-term assumptions about declining AI compute costs
🔹 Treat AI availability as a strategic dependency, not a utility
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.wsj.com/tech/the-chinese-company-taking-on-the-worlds-memory-chip-giants-78dfea55: January 20, 2026
Nvidia Stock Slips as Chipmaker Launches $1B AI Lab With Eli Lilly
Barron’s / Wall Street Journal — Jan. 12, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
Nvidia’s new $1B AI drug-discovery lab with Eli Lilly underscores AI’s expansion into life sciences—even as investors stay focused on chip demand, geopolitics, and execution risk.
Executive Summary
Nvidia announced a five-year, up to $1 billion investment with pharmaceutical giant Eli Lilly to create a joint AI lab focused on biology and chemistry modeling, signaling deeper convergence between AI infrastructure and life sciences. The lab will combine Nvidia’s AI engineers with Lilly’s medical and scientific experts to accelerate drug discovery through large-scale computational modeling.
Despite the strategic importance, Nvidia’s stock barely moved, reflecting investor concerns about China-related chip sales, broader AI demand sustainability, and the capital intensity of AI expansion. Nvidia leadership emphasized that AI demand remains strong across hyperscalers, sovereign customers, and China-specific chips, but near-term market sentiment remains cautious.
For executives, the signal is clear: AI’s value creation is increasingly verticalized, moving beyond generic models into industry-specific, high-stakes domains like healthcare—where compute, data, and domain expertise must converge.
Relevance for Business
For SMB leaders, this highlights how AI innovation is shifting toward specialized ecosystems, not just tools. Even if you’re not in healthcare, expect similar AI lab models to emerge in manufacturing, logistics, finance, and legal services, reshaping competitive dynamics and vendor relationships.
Calls to Action
🔹 Monitor how AI vendors are embedding domain expertise, not just selling general-purpose tools
🔹 Expect higher AI costs tied to specialization, not commodity pricing
🔹 Evaluate partnerships that combine AI + industry data, not standalone platforms
🔹 Plan for AI governance where models directly influence regulated decisions
🔹 Track geopolitical risk as a real variable in AI availability and pricing
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.wsj.com/wsjplus/dashboard/articles/nvidia-stock-price-ai-chips-china-8bfa9df6: January 20, 2026
How Google and Shopify Could Spark an Agentic Commerce Boom
Investor’s Business Daily — Jan. 12, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
Google and Shopify are laying the groundwork for AI agents that can autonomously shop, transact, and manage checkout—reshaping how digital commerce works.
Executive Summary
Google and Shopify unveiled a Universal Commerce Protocol (UCP) at NRF 2026, an open standard enabling AI agents to browse, select, and complete purchases on behalf of users across merchant platforms. This marks a significant step toward agentic commerce, where software—not humans—executes transactions.
The initiative builds on Google’s massive Shopping Graph (50B+ products) and Shopify’s merchant infrastructure, while addressing trust and authorization challenges through cryptographically signed contracts and payment authentication layers. Major retailers—including Lowe’s, Kroger, and Papa John’s—are already piloting agent-enabled customer experiences.
Analysts estimate agentic commerce could represent $3–$5 trillion annually by 2030, positioning AI agents as a new economic actor rather than a passive recommendation engine.
Relevance for Business
For SMBs, this is a commerce model shift, not a feature update. Purchasing decisions may soon be optimized by AI agents comparing price, availability, loyalty benefits, and terms—reducing brand differentiation and increasing platform dependence.
Calls to Action
🔹 Audit whether your products are AI-agent discoverable
🔹 Prepare for AI-driven checkout flows, not human UX
🔹 Reassess pricing and promotions in a machine-negotiated market
🔹 Track platform dependency risk (Google, Shopify, Amazon)
🔹 Begin governance planning for AI-to-AI transactions
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.wsj.com/wsjplus/dashboard/articles/shopify-builds-momentum-in-agentic-ai-shopping-at-nrf-2026-134126171306145904: January 20, 2026GOOGLE EMERGES AS THE AI MARKET LEADER AS ALPHABET CROSSES $4 TRILLION
The Wall Street Journal — Jan 12–13, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
Google has decisively re-established itself as a top-tier AI leader—combining model performance, infrastructure control, and ecosystem reach—and markets are rewarding it accordingly.
Executive Summary
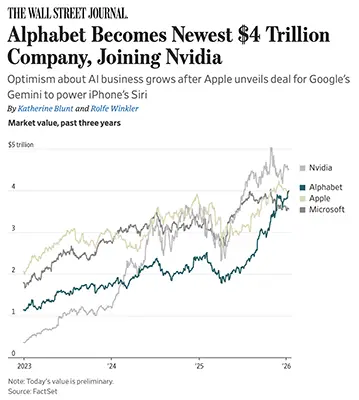
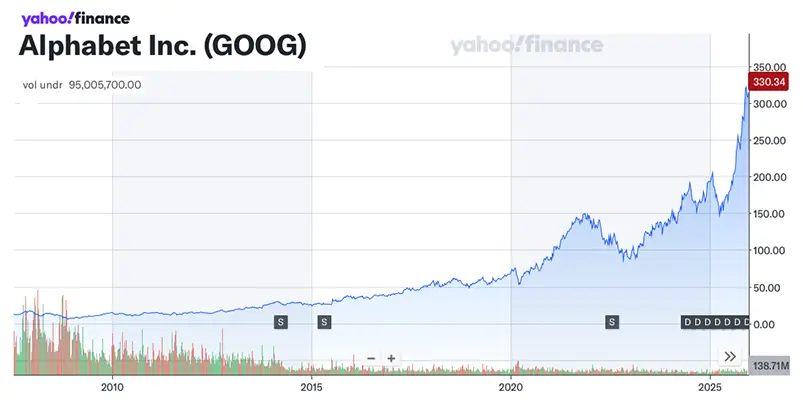
Alphabet’s surge past a $4 trillion market valuation reflects more than investor enthusiasm—it signals a strategic shift in the AI landscape. After early concerns that Google was falling behind OpenAI and others, the company has rebounded forcefully through the rapid advancement of its Gemini AI models, proprietary Tensor Processing Units (TPUs), and deep integration across consumer and enterprise products.
A pivotal moment came with Apple’s decision to use Gemini to power future versions of Siri, validating Google’s AI capabilities at scale. Gemini 3 has now surpassed many competitors on benchmark tests and reached 650+ million monthly users, driven by performance improvements and popular tools like image generation. Unlike many rivals, Google controls the full AI stack—models, chips, cloud infrastructure, and distribution—allowing it to deliver AI at lower cost and massive scale.
Financially, this AI momentum is translating into results. Alphabet’s cloud business is growing rapidly, advertising remains resilient, and investor confidence has flipped from skepticism to conviction. Google is no longer just defending its core business—it is reshaping it around AI.
Relevance for Business
For SMB executives, Google’s rise matters because it strengthens the case for AI platforms embedded into everyday tools—search, productivity, cloud services, and mobile devices. Google’s scale and cost advantages may translate into more accessible, competitively priced AI services for smaller organizations. At the same time, consolidation around a few dominant AI providers increases vendor dependence and strategic lock-in risks.
Calls to Action
🔹 Reassess Google’s AI tools across Workspace, Cloud, and mobile platforms
🔹 Compare AI vendor pricing as Google leverages TPUs to undercut GPU-heavy rivals
🔹 Monitor ecosystem consolidation and dependency risks
🔹 Watch Apple–Google AI integration for downstream product impacts
🔹 Align AI adoption with long-term platform strategy, not short-term features
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
<a href="https://www.barrons.com/articles/google-stock-price-alphabet-4-trillion-74a8ba6b: January 20, 2026<a href="https://www.wsj.com/tech/ai/google-4-trillion-valuation-0a022302: January 20, 2026
<a href="https://www.msn.com/en-us/news/technology/google-is-now-the-ai-top-company-alphabet-stock-keeps-rising-past-4-trillion-milestone/ar-AA1U7HQx: January 20, 2026

GOOGLE MOMENTUM CONTINUES AMID APPLE DEAL AS SOFTWARE STOCKS ARE HAMMERED
Investor’s Business Daily — January 13, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
Google’s AI partnership with Apple reinforces its platform dominance, while generative AI tools threaten traditional software business models.
Executive Summary
Alphabet’s stock hit record highs after Apple confirmed it will use Google’s Gemini AI models to power the next version of Siri, strengthening Google’s position as a foundational AI platform . Wall Street firms raised price targets, citing Google’s expanding AI footprint across search, cloud, advertising, and consumer services.
At the same time, software-as-a-service stocks sold off sharply, as investors worried that AI-native tools from companies like OpenAI and Anthropic could replace or commoditize traditional enterprise software. Anthropic’s launch of a general-purpose AI coding assistant intensified concerns that AI will undercut existing vendors rather than merely augment them.
The market reaction reflects a broader shift: value is consolidating at the AI platform layer, while downstream software faces margin pressure and competitive disruption.
Relevance for Business
For SMB executives, this signals that AI leverage increasingly comes from platform alignment, not niche tools. Choosing vendors with strong AI infrastructure backing may matter more than feature depth.
Calls to Action
🔹 Evaluate which AI platforms your vendors depend on
🔹 Expect pricing pressure on traditional SaaS tools
🔹 Favor vendors that integrate deeply with leading AI ecosystems
🔹 Plan for faster software obsolescence cycles
🔹 Treat AI platform risk as a strategic dependency
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.investors.com/news/technology/google-stock-momentum-apple-siri-record-high/: January 20, 2026
FIVE WAYS AI CAN SUPPORT EMPLOYEE WELL-BEING (AI-ADJACENT / APPLIED AI)
Fast Company — October 20, 2025
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
AI’s most durable workplace value may come from improving employee well-being—not just productivity—when deployed intentionally and ethically.
Executive Summary
Fast Company outlines five practical ways AI can enhance employee well-being, from simplifying benefits access to enabling safer reporting, real-time feedback, and early conflict detection . The article argues that organizations will thrive not by using AI most aggressively, but most intentionally.
Examples include AI copilots that clarify benefits eligibility, anonymous reporting tools that reduce fear of retaliation, and sentiment analysis systems that surface team issues before they escalate. Crucially, the piece emphasizes human-first integration, where AI supports—not replaces—human judgment.
While optimistic, the article implicitly acknowledges risks: privacy, surveillance, and misuse. The distinction lies in governance—AI should augment trust, not monitor or control behavior.
Relevance for Business
For SMB leaders, this provides a blueprint for low-risk, high-impact AI use that improves retention, morale, and organizational resilience without entering legally sensitive domains like automated therapy.
Calls to Action
🔹 Focus AI pilots on support functions, not evaluation
🔹 Ensure transparency around data use
🔹 Keep humans in decision-making loops
🔹 Use AI to surface patterns—not police individuals
🔹 Align AI deployment with culture and values
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
<a href="https://www.fastcompany.com/91421078/5-ways-ai-can-support-employee-well-being: January 20, 2026
NVIDIA PARTNERS WITH ELI LILLY TO LAUNCH $1B AI DRUG DISCOVERY LAB
TechTarget — January 12, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
Nvidia’s $1B partnership with Eli Lilly shows how AI is moving from general tools to deeply embedded, industry-specific innovation engines.
Executive Summary
Nvidia and Eli Lilly announced a five-year, $1 billion AI co-innovation lab designed to accelerate drug discovery using Nvidia’s BioNeMo platform and next-generation Vera Rubin AI chips . The lab will allow scientists to simulate biological and chemical interactions digitally before physical testing begins.
The partnership reflects a broader trend: AI’s biggest gains now come from vertical integration, where compute, proprietary data, and domain expertise converge. Lilly had already planned a supercomputer using more than 1,000 Nvidia GPUs, signaling that pharma companies increasingly view AI as core R&D infrastructure—not optional experimentation.
This model contrasts with generic AI adoption. It suggests future breakthroughs will favor companies that build AI into their operating core, not just their productivity stack.
Relevance for Business
For SMB leaders, this is a roadmap: AI delivers outsized returns when tailored to specific workflows, not when deployed as a one-size-fits-all tool.
Calls to Action
🔹 Identify high-value workflows for domain-specific AI
🔹 Expect AI vendors to offer verticalized solutions
🔹 Budget for AI as infrastructure, not software
🔹 Watch healthcare AI as a leading indicator for other industries
🔹 Evaluate partnerships over standalone AI tools
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.techtarget.com/pharmalifesciences/news/366636927/Nvidia-partners-with-Lilly-to-launch-1B-AI-drug-discovery-lab: January 20, 2026
ALIBABA UPDATES ITS QWEN AI APP. HOW IT’S FOLLOWING MICROSOFT AND ALPHABET
The Wall Street Journal — January 15, 2026
TL;DR / Key Takeaway:
Alibaba’s Qwen upgrade shows that AI-powered shopping agents are becoming a global standard.
Executive Summary
Alibaba updated its Qwen AI app to allow users to complete tasks like ordering groceries and booking travel directly through the chatbot . The move mirrors similar efforts by OpenAI, Google, Microsoft, and Shopify to integrate AI agents with commerce platforms.
This reflects a broader push toward agentic AI—systems that don’t just recommend actions but execute them. By tightly integrating Qwen into its ecosystem, Alibaba is positioning AI as a transaction layer, not just a discovery tool.
While Alibaba’s stock reaction was muted, the strategic signal is clear: AI-driven commerce is becoming infrastructure, not an experiment.
Relevance for Business
SMBs should expect AI-mediated purchasing and customer journeys to become standard across platforms.
Calls to Action
🔹 Prepare for AI-driven customer interactions
🔹 Review e-commerce integrations for agent readiness
🔹 Monitor platform dependency risks
🔹 Expect faster, automated buying cycles
🔹 Reassess UX for AI-first discovery
Summary by ReadAboutAI.com
https://www.barrons.com/articles/alibaba-stock-qwen-ai-microsoft-alphabet-bfc0713a: January 20, 2026https://www.wsj.com/tech/chinas-alibaba-links-qwen-ai-app-to-vast-consumer-ecosystem-17b4f942: January 20, 2026
Closing: AI update for January 20, 2026
Taken together, these developments show AI settling into its role as infrastructure: embedded in assistants, agents, commerce protocols, and even national security in ways that will be difficult to unwind. For SMB executives and managers, the real work now is to pick platforms carefully, build governance early, and pilot agents in controlled, high-leverage workflows before this new infrastructure quietly makes those choices for you.
At the same time, several articles underscore the friction points emerging as AI scales. Leadership concentration around figures like Sam Altman, growing skepticism about AI-generated code quality, visible stylistic “tells” in AI-written communication, and early adoption of AI in courts all point to the same reality: trust, accountability, and oversight now matter as much as capability. The question for organizations is no longer whether AI can be used, but how responsibly, transparently, and sustainably it is deployed—and what new risks are introduced when automation touches law, identity, labor, and decision-making. Together, these stories frame AI not as a distant future technology, but as a present-day system that executives must actively manage.
All Summaries by ReadAboutAI.com
↑ Back to Top